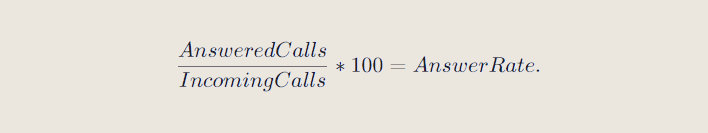CX Glossary
Whether it's calls, chats, emails, there's a lot of jargon that can get you stumped. Brush up on some terms that we commonly use. Then measure them with Happitu's CX solutions.
Learn HowAn abandoned call is when the caller hangs up before reaching an agent, usually due to a long wait, caller interruption, or recognition of a misdialed call.
Short Abandons
Short Abandons are calls abandoned within a specific threshold (usually the first 5 to 15 seconds) and are not typically part of the abandonment rate calculation.
Calculating Abandoned rate
Abandonment rate refers to the percentage of incoming calls disconnected by the caller before interacting with an agent or reaching a call queue. This can be expressed in the following formula:

Artificial intelligence is the ability of a computer or computer-controlled robot to complete tasks commonly associated with human beings. Specific applications of AI include natural language processing (NLP), automated speech recognition (ASR), sentiment analysis, and machine vision.
Agent Overtalk is a measure of how much an agent speaks while a customer is speaking during a phone call. The time is typically measured in seconds and then expressed as a percentage of the overall talk time of the call.
Referred to as Auto Dialers or simply Dialers, Call Center Automatic Dialers are software that can automate outbound calls from a lead list or database. They come in different types, many of which are configurable and can be integrated with your CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system.
An auto dialer can be used to either leave a pre-recorded message on their number when the call is answered or connect the customer to a live agent.
Predictive Dialer
A Predictive Dialer is specialist telephony equipment for managing outbound calls. The term predictive means that the dialer will phone the telephone number of the customers you want to contact, and only when the phone is answered by a person will the call then be directed to an agent to answer. An algorithm is used to predict when an agent is likely to become free and dials in anticipation of this so that the non-productive time that an agent spends between calls is minimized.
Soft skills are the conversational skills an agent demonstrates throughout a call. They can include call control, empathy, rapport building, etc.
Average contacts per hour is a measure of agent productivity and is calculated by dividing the number of contacts that the agent handled with the total number of hours the agent worked.
Availability measures how much agent time is spent between customer interactions waiting for the next inbound interaction. Formula:

After-Call Work (ACW), is a set of necessary tasks that need to be completed after an agent interacts with the customer. These may include updating the system, logging the reason for contact and outcome, updating colleagues, and scheduling follow-up actions.
This is also called “Wrap”, “Wrap-up”, and “Post-Call Processing” (PCP).
Customer SATisfaction (CSAT) is the elder statesman of "Voice of the Customer" surveys and is similar to just about anything you rate online today with a 1-5 stars scale. It simply asks the customer how satisfied they were with their interaction and provides response options from 1 (very unsatisfied) to 5 (very satisfied). Like CES, there are alternate methods to measure CSAT, including a 10-point scale and an emoji scale. CSAT is still considered a reliable metric to understand customer sentiment for a given interaction.
Learn more about common post interaction survey mistakes.
Call guides provide call center agents to access information and provide a workflow and/or scripting for them to follow during the call to ensure they resolve issues efficiently and to completion.
Call closing refers to the phrasing just prior to the termination of a call between the customer and agent. This may include an offer of further assistance, appreciation, and company branding. Closing statements differ according to the nature and requirements of individual business units.
Direct Inward Dialing (DID) is a communication service that connects a set of external telephone numbers to a private branch exchange (PBX). Employing DID technology, telephone numbers can be assigned dynamically without additional external phone lines.
Dead air is defined as the period of silence during a contact center interaction when neither the customer nor the agent is interacting.
A dialed number Identification service (DNIS) is a service offered by telecom providers to their commercial customers, letting them know what number was dialed for each incoming call. The data is sent as a series of touch tone digits along with the call and interpreted at the destination by the private branch exchange (PBX).
AHT stands for Average Handle Time. Because individual calls can have different demands, an average for a specified time, often a month, is used to determine efficiency. To calculate handle time take After Call Work (Wrap), Talk Time, and Hold Time. While most KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are ideally as low as possible or as high as possible, AHT is more of a Goldilocks metric - you want it to be "just right" within a target range. High AHT is a sign of inefficiency while low AHT often means we're not actually doing everything we need to do.
The time it takes the contact center to respond to asynchronous customer interactions like email.
RTWN - Response Time When New
RTWN is a metric that some contact centers use to calculate the average time it takes to respond to a new customer.
This is measured separately from Response Time because some companies aim to offer speedy assistance to new customers who are more likely to need support in using the product/service.
Speech analytics is the automated process of analyzing conversations. The process is primarily used by customer contact centers to surface information in client interactions aimed to improve future communications.
Service Level is the percentage of calls (or other contacts) answered within a given timeframe. Outsourced Contact Centers often operate under a Service Level Agreement (SLA) that guarantees a minimum Service Level measured over a period of time, typically a month.
Acceptable service levels can vary widely by channel. For the voice channel, typical Service Level Agreements are 80/3080/30 (80% of calls answered in 30 seconds or less) or 80/6080/60 (80% of calls answered within 60 seconds or less).
Low Service Levels often lead to high Abandon Rate because customers are waiting in queue too long to reach an agent.
While Service Level is a relatively simple measure, the variables to achieve a specific Service Level can be quite complicated and include forecasted volume, contact arrival patterns, agent staffing, shrinkage (percent of agents scheduled who don't actually work their shift), Occupancy, Average Handle Time, and Schedule Adherence.